high-voltage-pulse-generator
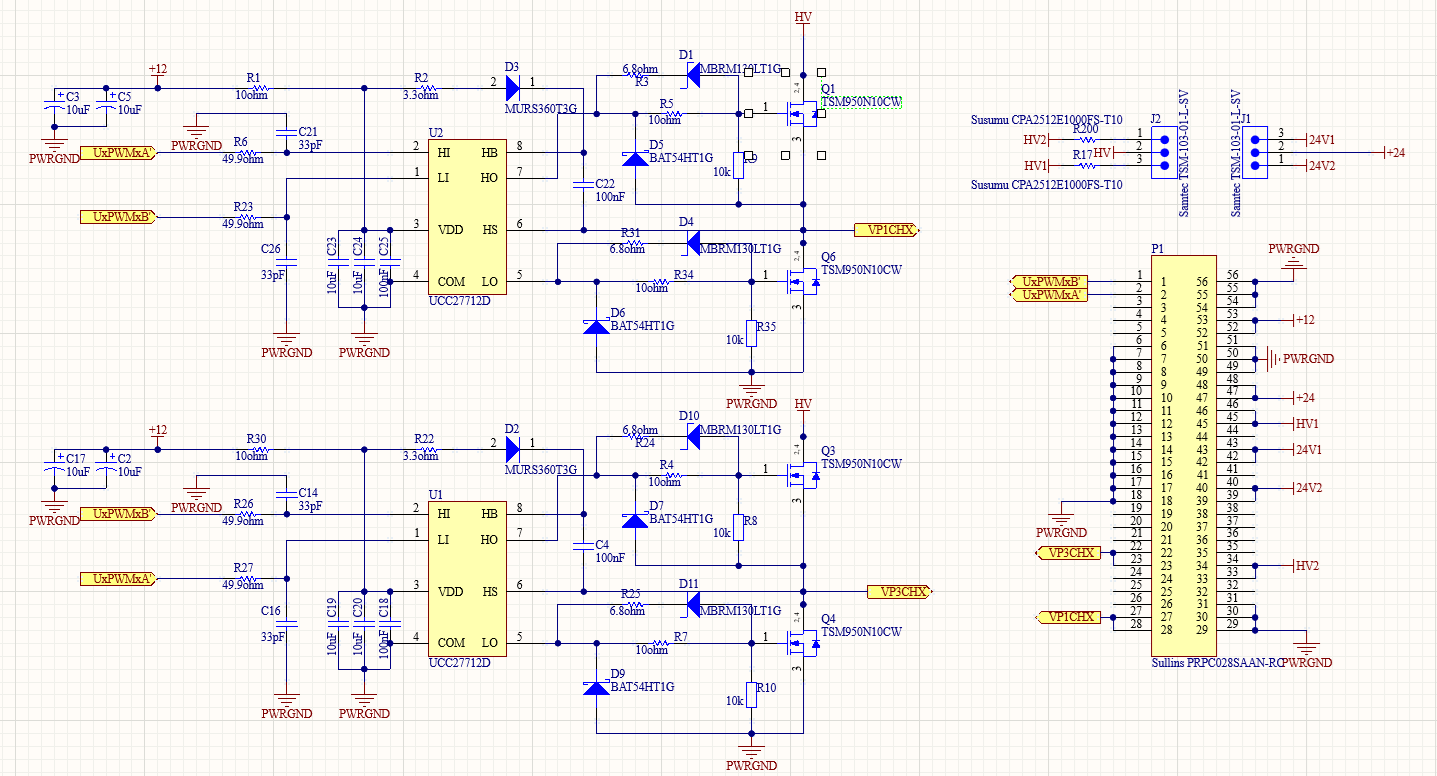
Schematic of Circuit
The design of the inverter was made considering the use of the half-bridge gate driver (UCC27712), which in this case allows for rapid switching of the gates/MOSFETs (Q1, Q4, Q3, Q6) through complementary PWM signals (UxPWMxA’, UxPWMxB’) coming from the ESP32. The load is the primary of the transformer and is connected to the VP1CHX and VP3CHX points. Additionally, the board is powered by a 12V/1A source and can operate with a continuous HV voltage of up to 100V, given the operational limitations of the MOSFET model TSM950N10.
! Caution ! If you choose to use a different MOSFET, the inverter could switch a continuous voltage of up to 600V. It is important to include the resistors R200 and R17, which limit the current entering the transformer’s primary, preventing it from burning out. In this case a 200 Ohm, 4W resistor is recommended.
i Note i The electronic board is designed to operate with two alternatives for high-voltage DC sources, HV1 and HV2. These voltages come from a control board, specifically from the voltage regulators MIC29302WU-TR (12-24V) and LT8361 (24V-80V), respectively. Alternatively, you can consider using a different DC voltage source that operates within a range of 12V-80V.